Backchannel story: ‘The Social Network Doling Out Millions in Ephemeral Money: Steemit’, October 2017
A feature story for Backchannel. Excerpt below.
The Social Network Doling Out Millions in Ephemeral Money
Steemit is a social network with the radical idea of paying users for their contributions. But in the crypto gold rush, it’s unclear who stands to profit.
Every time you log onto Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter to share a photo or post an article, you give up a piece of yourself in exchange for entertainment. This is the way of the modern world: Smart companies build apps and websites that keep our eyeballs engaged, and we reward them with our data and attention, which benefit their bottom line.
Steemit, a nascent social media platform, is trying to change all that by rewarding its users with cold, hard cash in the form of a cryptocurrency. Everything that you do on Steemit—every post, every comment, and every like—translates to a fraction of a digital currency called Steem. Over time, as Steem accumulates, it can be cashed out for normal currency. (Or held, if you think Steem is headed for a bright future.)
The idea for Steemit began with a white paper, which quietly spread among a small community of techies when it was released in March 2016. The exhaustive 44-page overview wasn’t intended for a general audience, but the document contained a powerful message. User-generated content, the authors argued, had created billions of dollars of value for the shareholders of social media companies. Yet while moguls like Mark Zuckerberg got rich, the content creators who fueled networks like Facebook got nothing. Steemit’s creators outlined their intention to challenge that power imbalance by putting a value on contributions: “Steem is the first cryptocurrency that attempts to accurately and transparently reward…[the] individuals who make subjective contributions to its community.”
A minuscule but dedicated audience rallied around Steemit, posting stories and experimenting with the form to discover what posts attracted the most votes and comments. When Steemit released its first payouts that July, three months after launch, things got serious.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are only worth whatever value people ascribe to them, so there was no guarantee that the tokens dropping into Steemit accounts would ever be worth anything. Yet the Steem that rolled out to users translated to more than $1.2 million in American dollars. Overnight, the little-known currency spiked to a $350 million market capitalization—momentarily rocketing it into the rare company of Bitcoin and Ethereum, the world’s highest-valued cryptocurrencies.
Today, Steem’s market capitalization has settled in the vicinity of $294 million. One Steem is worth slightly more than one United States Dollar, and the currency remains a regular presence at the edge of the top 20 most traded digital currencies.
It’s a precipitous rise for a company that just 18 months ago existed only as an idea in the minds of its founders. More than $30 million worth of Steem has been distributed to over 50,000 users since its launch, according to company reports. It’s too early to know whether Steemit can hold onto its users’ interest and its market value. But its goal—upending a model built by social media giants over decades of use in favor of a more populist system—is significant in itself. By removing the middlemen and allowing users to profit directly from the networks they participate in, Steemit could provide a roadmap to a more equitable social network.
Or users could get bored or distracted by something newer and shinier and abandon it. The possibility of a popped bubble looms over every cryptocurrency, and the bubbles are filled with both attention and speculative investment. Steemit’s value is based on money that its founders have virtually willed into existence. Fortunes could vanish at any moment, but someone stands to get rich in the process.
To read the full story, visit Backchannel. Above illustration credit: Lauren Cierzan.


 In Digital Vertigo [pictured right], Anglo-American entrepreneur Andrew Keen takes a critical stance against the technologists behind social networking tools such as Facebook and Twitter, for reasons exemplified in the book’s subtitle. Keen knows his topic from the inside: on the cover the title is presented as a Twitter hashtag and the author’s name as
In Digital Vertigo [pictured right], Anglo-American entrepreneur Andrew Keen takes a critical stance against the technologists behind social networking tools such as Facebook and Twitter, for reasons exemplified in the book’s subtitle. Keen knows his topic from the inside: on the cover the title is presented as a Twitter hashtag and the author’s name as  Conversely, British novelist Nick Harkaway tries his hand at long-form nonfiction for the first time in The Blind Giant [pictured right], and strikes on a narrative that immediately grips the reader. Using tight language and evocative descriptions, Harkaway’s introduction is a nightmare vision of a dystopian, tech-led society where “consciousness itself, abstracted thought and a sense of the individual as separate from the environment” are all withering away. A contrasting vision of a “happy valley” follows, and is just as realistic and compelling.
Conversely, British novelist Nick Harkaway tries his hand at long-form nonfiction for the first time in The Blind Giant [pictured right], and strikes on a narrative that immediately grips the reader. Using tight language and evocative descriptions, Harkaway’s introduction is a nightmare vision of a dystopian, tech-led society where “consciousness itself, abstracted thought and a sense of the individual as separate from the environment” are all withering away. A contrasting vision of a “happy valley” follows, and is just as realistic and compelling.
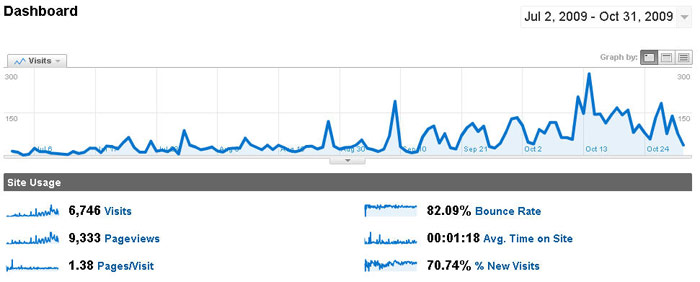
 A couple of months ago I undertook a
A couple of months ago I undertook a 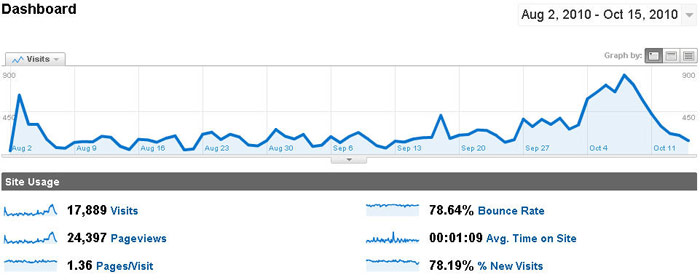
 This year, One Movement Word’s blog content was split into the following categories – click for further info:
This year, One Movement Word’s blog content was split into the following categories – click for further info: and by far the best music industry panel I’ve witnessed. Which doesn’t sound that impressive, really, but trust me: Nick and his panelists touched on some brilliant, universally-understood topics, like pursuing your passion, the nature of independence, and being kind to others without expectation of repayment. I’ll say no more; you’ll have to read my
and by far the best music industry panel I’ve witnessed. Which doesn’t sound that impressive, really, but trust me: Nick and his panelists touched on some brilliant, universally-understood topics, like pursuing your passion, the nature of independence, and being kind to others without expectation of repayment. I’ll say no more; you’ll have to read my  For the last couple months, I’ve been reading a book by
For the last couple months, I’ve been reading a book by  I’ve been online for like 10 years, and I’m only just beginning to consciously pay attention to this stuff. Cumulative advantage dictates that the more time you spend online building meaningful relationships and contributing to the internet, the easier it’ll be to get what you want.
I’ve been online for like 10 years, and I’m only just beginning to consciously pay attention to this stuff. Cumulative advantage dictates that the more time you spend online building meaningful relationships and contributing to the internet, the easier it’ll be to get what you want.